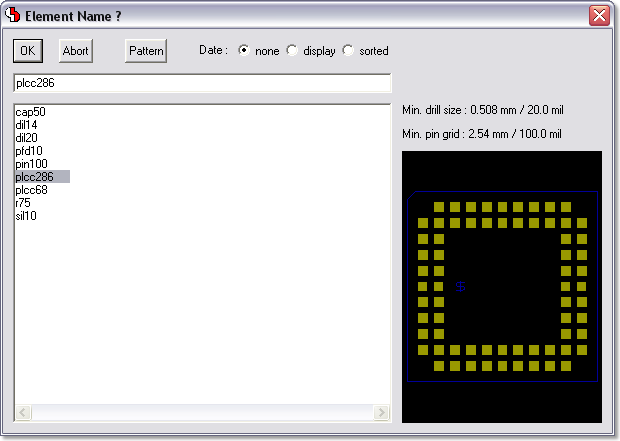
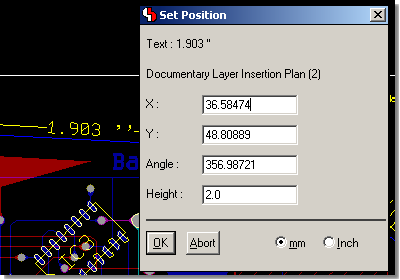
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Product Information
Contents
Last Change
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Screenshots
The following pictures show typical screen shots of the
Bartels AutoEngineer® software.
The basic BAE user interface is identical on the supported platforms. However, through the
User Language which is freely available with every BAE system, the features for customizing the menu layout and adding new functions virtually unlimited. We are encouraging and supporting users in adapting the menu to their special requirements. I.e., customer-specific BAE menus are commonplace...
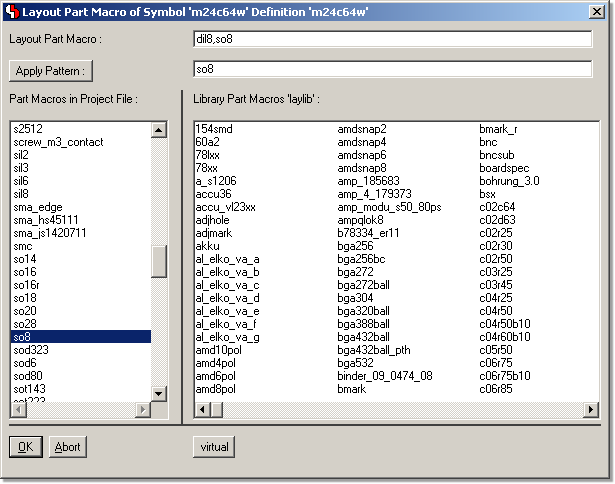
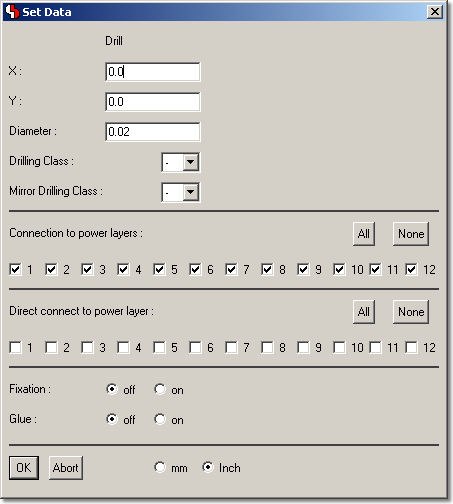
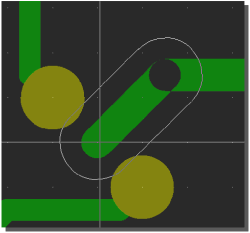
Bartels AutoEngineer Main Menu
Figure 1 shows a screen shot from the
BAE HighEnd main menu screen on
Windows XP. The
function starts additional processes coupled with the current process, thus allowing for inter-module communications such as cross-highlighting between the
Schematic Editor and the
PCB Layout Editor. The
CAM View module including Gerber viewer, panelization functions and manufacturing data optimizers is provided with every
AutoEngineer layout system at no additional cost. The menu below also shows the function for activating the optional
IC/ASIC Design system:
Figure 1: Bartels AutoEngineer HighEnd Main Menu
Bartels AutoEngineer Schematic Capture
Figure 2 shows a typical
Schematic Capture session. The toolbar at the left provides buttons for frequently used display and file functions, design view management facilities, and a feature for automatic part attribute settings, all of which is designed and can be fully customized through
User Language. Please note the resistor attributes and the bus connection to the processor IC in the schematic plan. The system automatically connects the individual bus lines based on the logical library description:
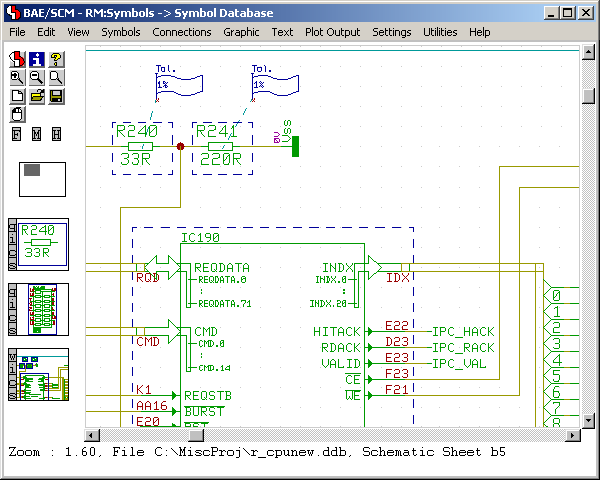
Figure 2: Bartels AutoEngineer Schematic Capture
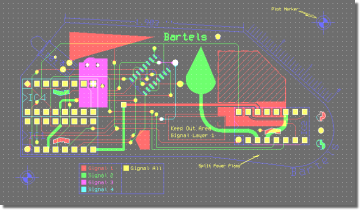
Bartels AutoEngineer PCB Layout
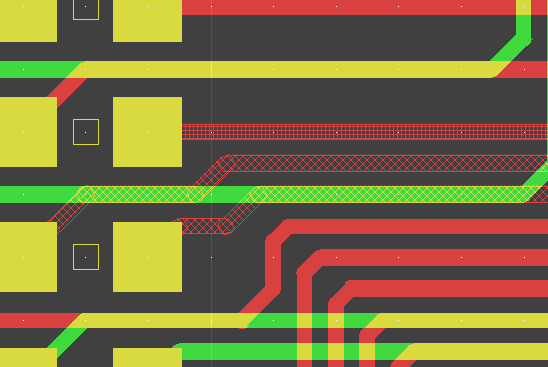
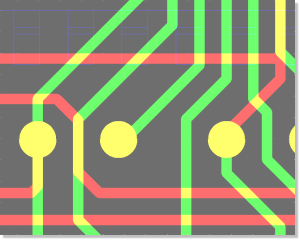
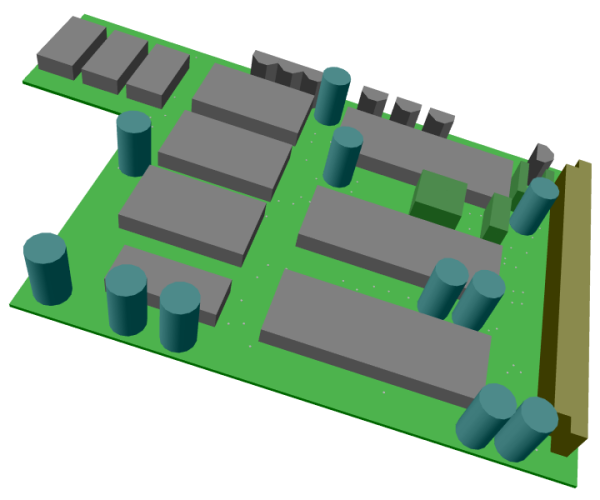
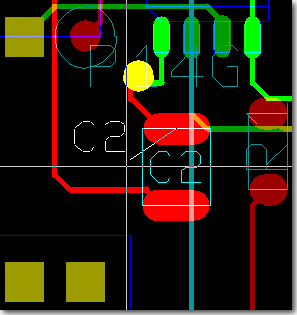
Figure 3 shows a typical
PCB Layout Editor window. The PCB layout displayed shows a mixture of possible design options, such as the use of surface mounted devices (SMDs), curved traces, negative split power planes, positive copper pour areas, irregular pad and copper shapes, etc. The DRC is able to handle all these online and in real time, as it is based on an incremental technology which also allows for multi-step
. The toolbar on the lefthand side is designed with
User Language and provides design view management facilities and buttons for frequently used display and file access functions:
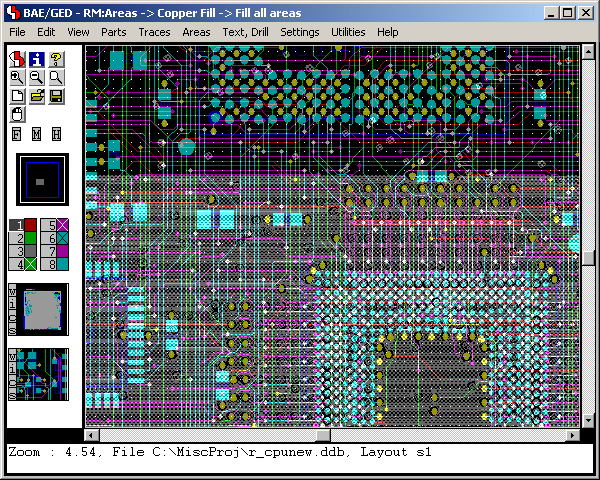
Figure 3: Bartels AutoEngineer PCB Layout
Bartels AutoEngineer ASIC/IC Design
An IC design module including real-time mask connectivity, GDS2 I/O, Standard Cell Placement with intelligent algorithms as well as routing using the
Bartels AutoEngineer in its IC design version is available as an option.
Figure 4 shows a typical IC mask layout
(Chip Editor) session.
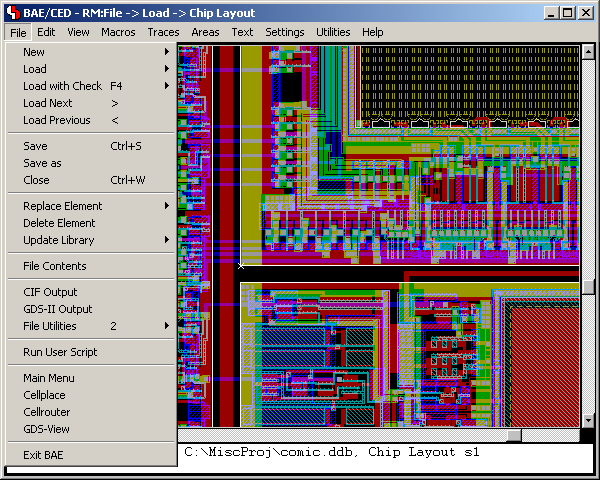
Figure 4: Bartels AutoEngineer ASIC/IC Design
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Design DataBase (DDB)
The following figures show the hierarchical structure of the
Bartels AutoEngineer object oriented Design DataBase (DDB). All design objects are stored in a single file, and each design object belongs to a certain class (e.g., drawing, symbol, etc.) and can inherit (include) symbols from the same or from other classes depending on the design context. Database and design objects can be manipulated independently from other objects and may be copied, extracted, included or deleted as required. The database knows about the design relations, i.e., copying a schematic sheet automatically copies inherited part and pin symbols. All database files, design or library, have the same file format. Whether a file is a design or a library file depends on its (contextual) content rather than on its file structure.
SCM Database Hierarchy
Figure 1 explains the schematic capture graphical object relations:
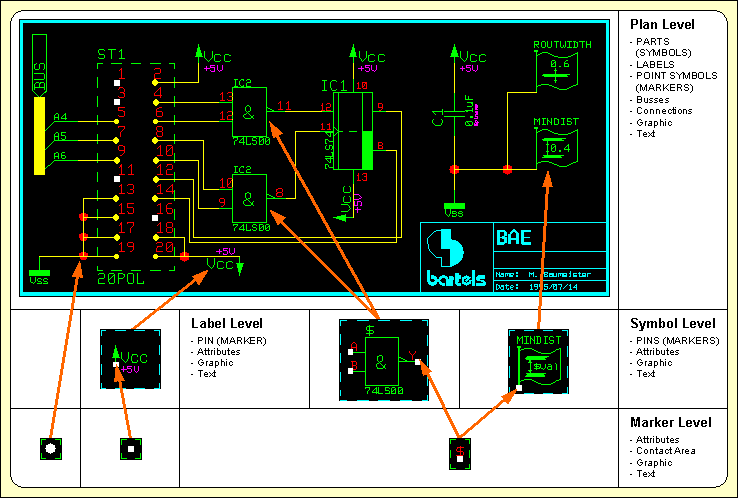
Figure 1: SCM Database Hierarchy
Logical Symbol/Part Definition
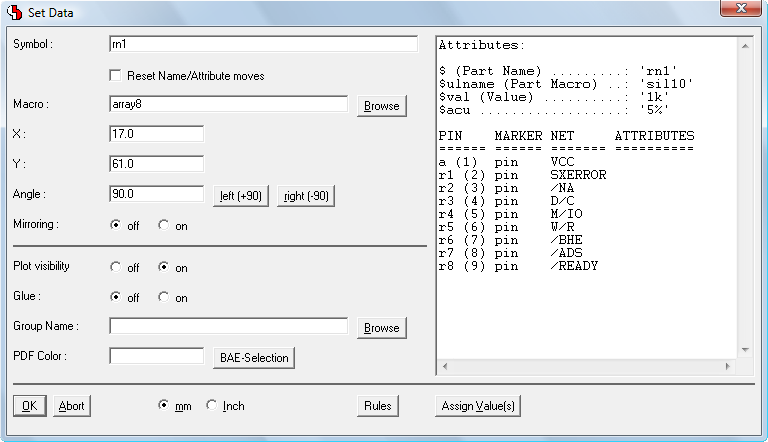
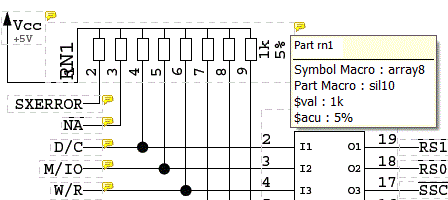
Figure 2 shows the relations between the logical and physical parts as well as an example for pin/gate/group swap information and power supply pins. This description can also be used to specify a fully hierarchical design, e.g., for ASICs or custom ICs:
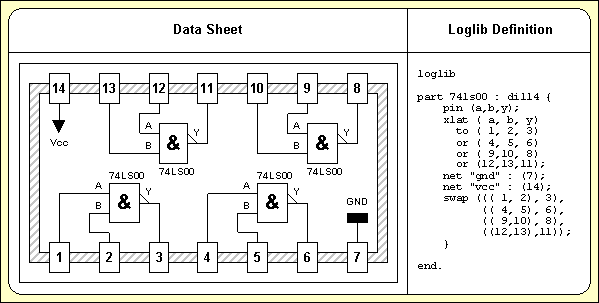
Figure 2: Part Data Sheet with Loglib Definition
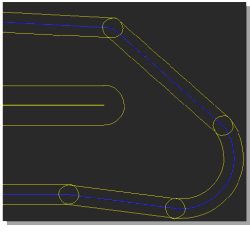
Layout Database Hierarchy
Figure 3 illustrates the construction of a printed circuit board. Arbitrarily shaped polygons can be created in any design hierarchy level. A polygon may also contain arcs, which are handled by the system as basic element types, i.e., all arc calculations are precise without using arc interpolation:
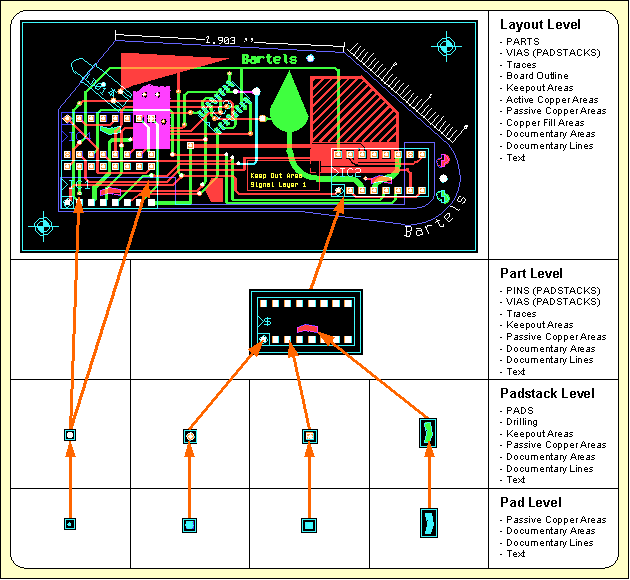
Figure 3: Layout Database Hierarchy
Bartels AutoEngineer Design System Data Flow
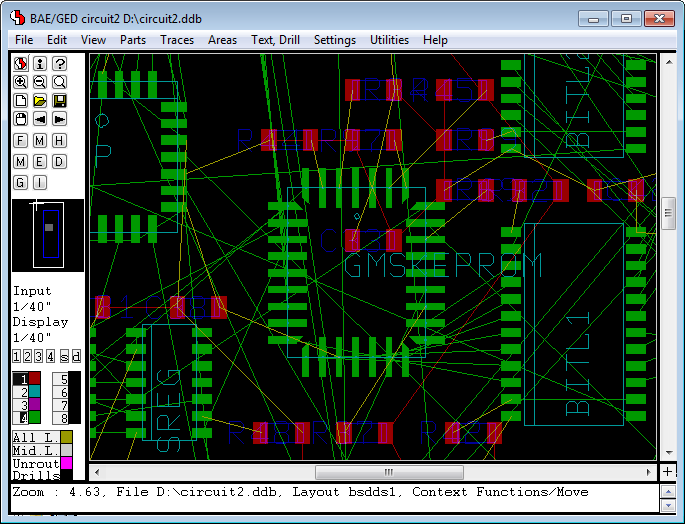
Figure 4 explains the overall dataflow within the complete design system including schematic capture and PCB design. Consider the central position of the
Job File which, at the end of the design process, contains all design-specific objects such as the schematic sheets, the PCB layout, the netlist data, and the job-specific library data:
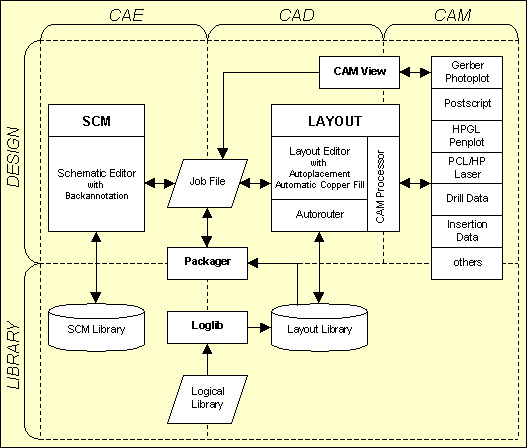
Figure 4: Bartels AutoEngineer System Flow Diagram
Please note that the same design file which contains all SCM and PCB data may also contain part lists or other table-oriented information. The
Bartels AutoEngineer database software includes an SQL engine which is able to bundle SQL table information transparently into its own object class and automatically build indices for quick database access. SQL database access optimization works with multiple tables, too. All database queries, whether to objects or via the SQL engine, are processed by a powerful variable key-length B-TREE algorithm. It is not necessary to copy symbol and/or part libarary data directly onto a schematic plan and/or a PCB layout, the schematic plan and the PCB layout objects only store (placement data) references to the placed symbols and/or parts. Library symbols and parts are copied into the design file when they are requested for placement for the first time. This automatically creates design-specific symbol and part libraries within the design file and leaves the designer with the opportunity to modify design-specific library elements without changing the original (master) library. The backup of a design is also much simplified, since a single DDB file ends up containing the complete SCM and PCB design and library data.
Bartels Autorouter®
The
Bartels Autorouter® was the first PC based protected mode rip-up/retry router. It is still the only one with selective Rip-Up/Cleanup/Backtracking. Previous versions were known as
Superoute of which thousands of licenses were sold worldwide.
Superoute modules were also modified by some source code OEM customers. Routers sold today under the name
Superoute no longer represent Bartels latest routing technology.
Bartels is the original source for all of the OEM versions resulting from more than 15 OEM contracts. The latest
Bartels Autorouter® version is integrated in the
Bartels AutoEngineer® CAD/CAE system.
Features
- Rip-Up/Retry Router with AI Backtracking.
- Intelligent routing provides high quality results.
- Backtracking allows the router to try several different solutions before committing to one. E.g., the router may remove a bunch of intersecting traces, trying an alignment without the risk of losing the previously best solution.
- Unique selective Rip-Up/Retry algorithm, superset of global Rip-Up and Shove.
- Unique selective Clean-Up algorithm.
- Any (user selectable) grid, sub-grid (between traces) routing, mixture of different grids, gridless pad connections.
- Net-oriented product, full T-connection support, incomplete traces for SMT-via preplacement.
- User selectable individual net/trace constraints for, e.g., width, length, structure, distance, priority.
- Real working optimization for really manufacturable PCB designs. Cross-net optimization (Cleanup).
- Automatic redesign of existing projects, stop, leave and/or re-start at any time (Re-Entrant routing).
- On-screen visible routing, rip-up, etc. Numerous user-controlled modes and routing cost factors.
- Supports any geometry of items including curved traces, polygon-with-arc obstacles and blind/buried/staggered vias with floating point accuracy.
- Rule based routing using Neural Net Technology.
- Both cell and shape based Routing algorithms, based on priority trees.
- Optional automatic Pin/Gate Swap during Routing.
- Optional Autoplacement.
- Bartels Autorouter® - Routing Examples
The router supports gridless placement of pads, obstacles and traces, cell based routing grid, routing with one or multiple cells in width to existing on-grid or off-grid pads and on-grid or off-grid traces. The off-grid feature is a combination of grid-based and gridless routing technologies and does off-grid routing of traces even in a cell-based environment, making it the ideal combination between cell-based and shape-based technologies.
Bartels Autorouter V6.2 - New Features
1 Rules for EMC Net Routing Area Classification
Integrated with the BAE schematic and PCB rule system, the
Bartels AutoEngineer supports automatic assignment of net classes based on library part/pin classifications and schematic tags to the actual design. Together with rules assigned to PCB areas, this allows for board design with EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) rules application.
Bartels Autorouter V6.0 - New Features
1 Dual Database for Contour/Shape based Routing
Increased use of SMT fine pitch parts has created a demand for a flexible grid routing technology. The previous versions of the
Bartels AutoEngineer used the following data representation:
- A one byte per cell per layer routing matrix (any basic grid may be chosen)
- Integer (matrix) coordinates routed trace representation
- Indexed floating point trace anchors (e.g., to fixed off-grid traces)
- Floating point fixed trace representation
- Floating point polygon pin and obstacle representation
In this case floating point coordinates permit what is called a "gridless" (shape/contour) representation. This database supports true floating point polygons/polylines including arcs for all data including prerouted fixed traces, however, with the exception of currently routed traces. The router can connect to off-grid junction points, including pins and fixed traces.
With the introduction of the sub-grid mode, the on-grid limit for routed traces was relaxed to half-grid (one-half) shifted traces, thus permitting proper handling of fine pitch SMT. However, this mode requires additional matrix memory and more computing time.
Competing products claiming to be "gridless" choose a multi-way (mostly four-way) geometrical tree approach which ends up in rectangular leafs. The advantage of this data representation is that rectangular data may indeed be represented with high resolution and routing is fast if trace and corner density is low. However, for high-density boards it requires even more memory than a matrix-based approach, and access time for allocation checks at certain board positions can increase excessively. The greatest pitfall, however, is the lack of efficient facilities for joining neighbouring rectangles, thus layout quality in true gridless mode often deteriorates dramatically, with 100% routing results becoming exceptional. This is especially true for non-rectangular (e.g., polygon) obstacles and 45 degree routing.
Our solution is to keep the matrix at the lowest possible density for strategic routing purposes, and to do the final artwork on a gridless database.
The
Bartels Autorouter V6.0 maintains a floating point database for routed traces parallel to the integer/matrix representation (dual database). The matrix allows for efficient routing and rip-up/retry with high quality results even for highest trace and/or ratsnet density. The floating point contour/shape routing database results in efficient board space usage by finding off-grid SMT channels and high quality SMT pad connections including long distance off-grid routing where required and/or applicable. The dual database combines the advantages of both concepts, thus giving significant improvement over both pure matrix and pure shape-based routing. The strategic trace routing is done via the matrix, thus both the advanced Lee algorithm which guarantees to find the least cost optimum way for a single trace, and the Bartels RipUp and CleanUp algorithms which detect optimum traces for rip-up and cleanup, can be used together with a non-rectangular shape-based database.
The dual database is an open end development. One of the next steps will be simultaneous maintenance of multiple routing matrices to reach even higher quality on mixed analog/digital boards. Further developments could yield the selective placement adjustment for certain parts to combine and thus gain additional trace channels.
2 Rule System with Neural Net Technology
The
Bartels Autorouter V6.0 is also called the
Neural Router because it may be combined with the
Bartels Rule System. The
Rule System applies one or more rules to system objects such as parts or traces. The rules are defined using a language similar to Prolog, however, with special operators to find not only all possible, but also optimum solutions to design-specific rule system queries or output requests.
The rules may be defined and assigned to individual items such as parts, nets, or traces as well as for the overall system, e.g., for cost factor and routing strategy control.
As the
Rule System uses a novel neural net approach to focus the rule evaluation on the probably best path, the
Bartels AutoEngineer combined with the
Rule System is called the
Bartels Neural Autorouter™.
3 Other Features
The
Bartels Autorouter V6.0 implements the pin/gate/group swap within the router depending on the routing results. If enabled, this feature permits routing of even the most complex boards, because the router gains an additional degree of freedom. The swaps done by the
Autorouter are reported by the output interface and
requests for correlating the schematic plan are automatically stored with the design.
Together with the introduction of the pin/gate/group swaps, a part-oriented input interface was implemented to permit placement optimizations by the router in future versions. The interface now maintains an additional attribute field (trace/via ident code) to support rather specific definitions such as traces on part level, a BAE-specific feature widely used for defining printed inductors.
A documented interactive routing functions interface is provided to implement the interactive single net/part routing features through the standard interface (used by the
Neural Autorouter module).
In addition to standard negative power planes and copper and copper pour areas, the
Autorouter now also supports split hierarchical negative power planes.
Bartels Autorouter®
Routing Examples
The following images shows some examples of PCB designs which were automatically routed with the
Bartels Autorouter®.
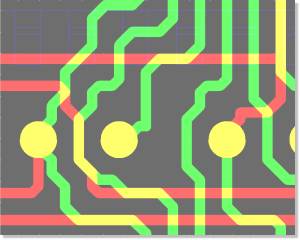
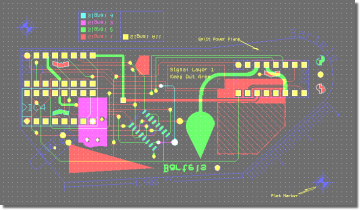
Bartels Autorouter Application Example - Medium Size Conventional Board
Figure 1a displays a medium size conventional printed circuit board with some manually pre-routed critical traces and power supply connections:
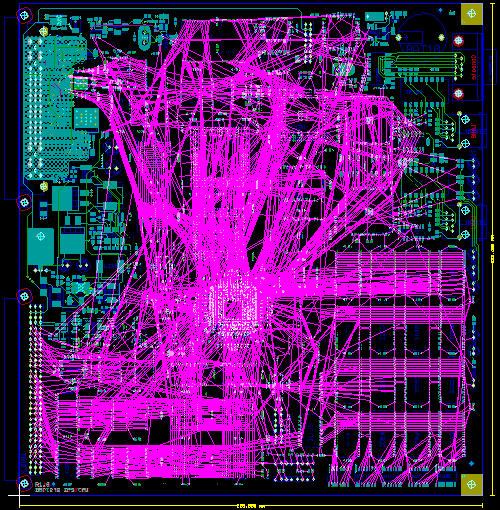
Figure 1a: Bartels Autorouter Application Example - Medium Size Conventional Board (unrouted)
Figure 1b shows the automatically routed version of the PCB layout from
figure 1a. The
Autorouter used four signal layers and two power planes:
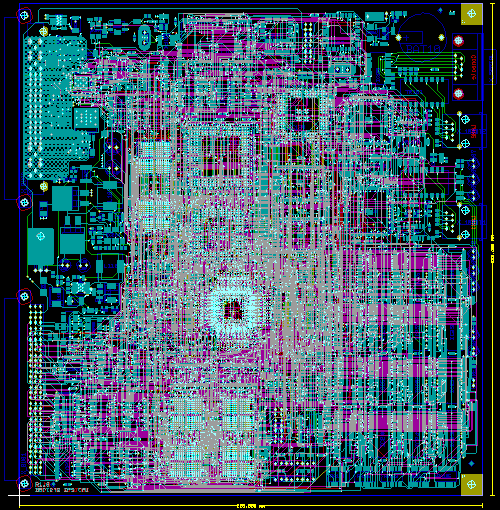
Figure 1b: Bartels Autorouter Application Example - Medium Size Conventional Board (automatically routed)
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 8.0
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 8.0.
Contents
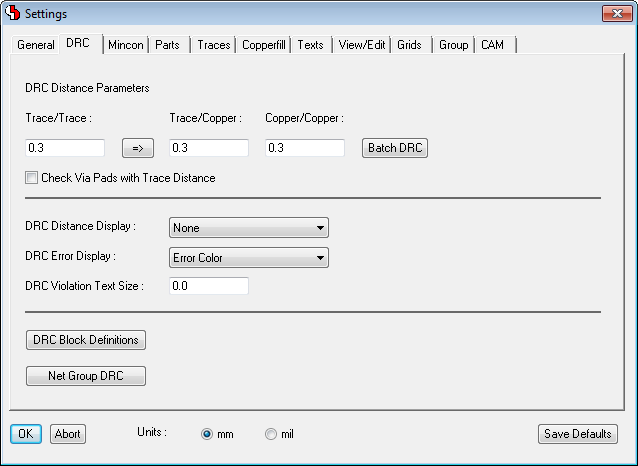
Improved Parameter Dialogs with Tab Controls
Draw Lines with Arrowheads
Right-aligned Text Placement
Labels included in Net Highlight
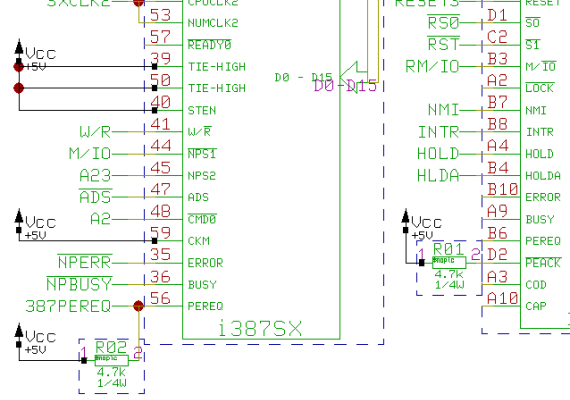
Labels included in Net Highlight - with Highlight Focus
 |
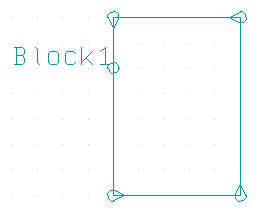
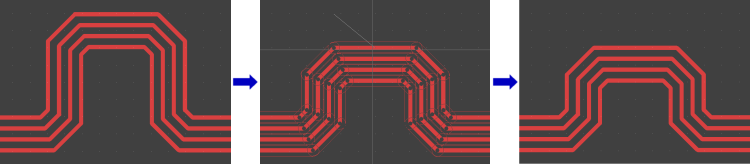
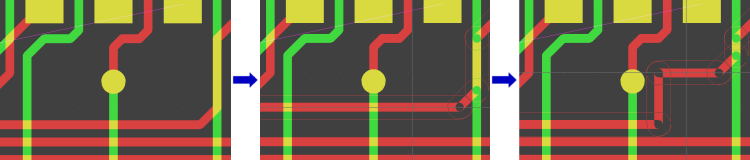
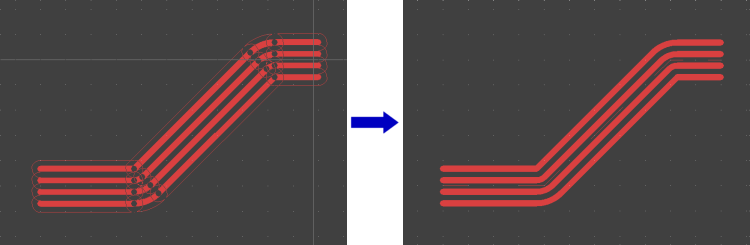
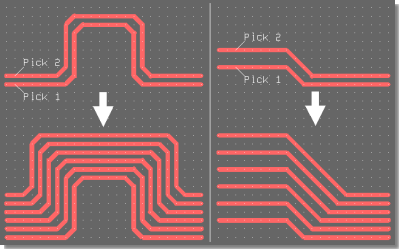
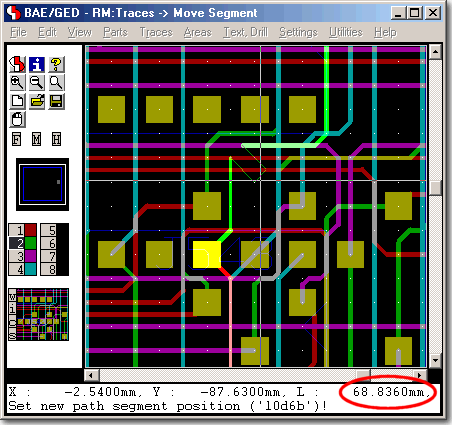
Move Trace Segment Bundles
Automatic Trace Segment Split at Obstacles
Bus Placement
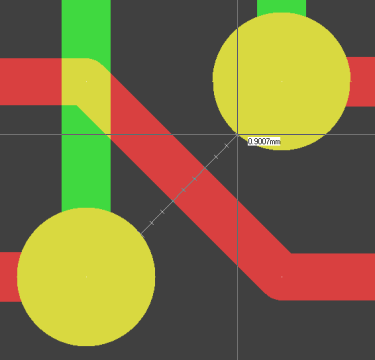
Distance Query Scale Marks for Clearance Distance Assessment
Trace Width to Pad Dimension Adjustement through s Key
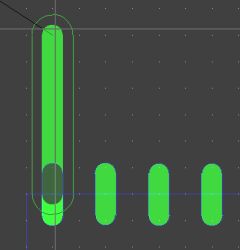
Filled Part Pad Display During Part Placement Operations
Part Online DRC During Part Placement Operations
Automatic Keepout Area Generation at Copper Pour Bottlenecks
Specific Fill Clearance for Impedance-controlled Traces
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 7.8
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 7.8.
Contents
Extended Clipboard Features
Clipboard - Attribute Transfer
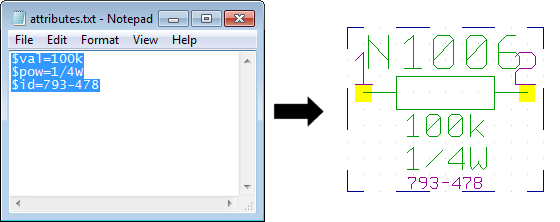 |
Clipboard - Coordinate Transfer
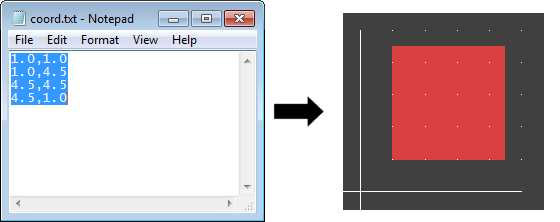 |
List View Dialog boxes with Sortable Columns
BAE HighEnd - Placed Symbol Indication
Pattern Display Options for Fixed and Glued Elements
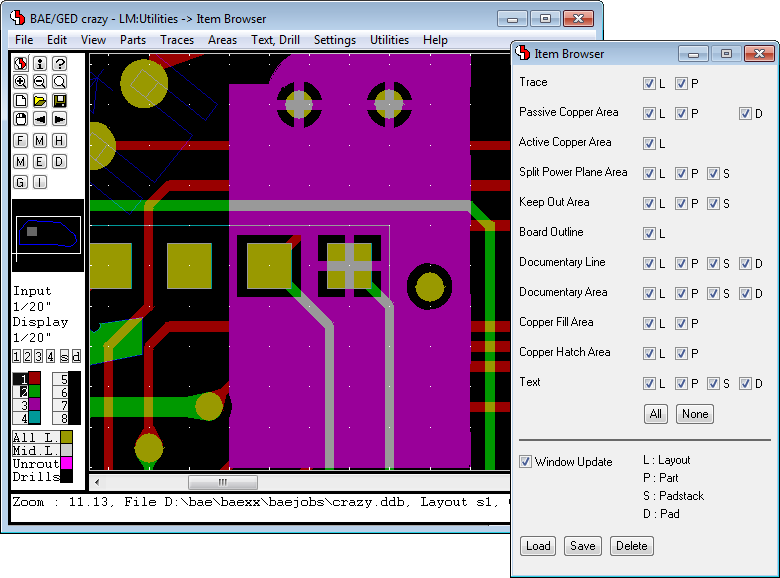
Item Browser with Element Type and Hierarchy Level Display Options
Airline Display Option Restriction to Airlines Ending in Viewport
Airline Display with Signal Layer Colors
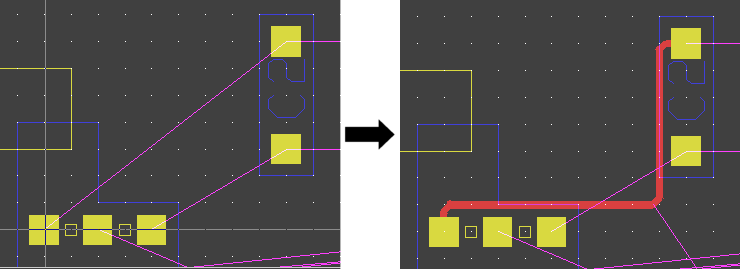
Point-to-Point Router
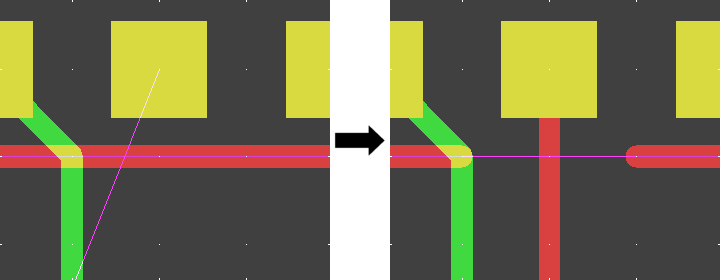
Clip Obstructing Traces when Placing New Trace
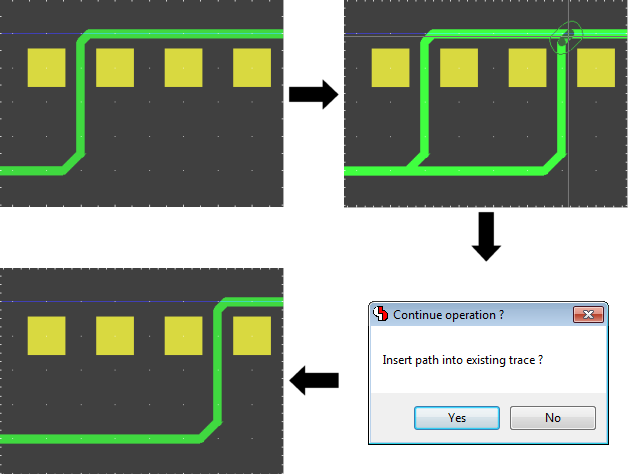
Insert Trace into existing Trace
Windows Print Output with Mixed Colors on White Background
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 7.6
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 7.6.
Contents
Additional Polygon Types supported by Draw Assistant
Arc Direction Polygon Edit Marker
Polygon Corner/Segment Drag & Drop Edit Mode
Windows Tooltips with Toolbar Data Display
Group and Error Highlight with Display Patterns
Symbol Move with Unroutes Display Option
Dialog with Text Properties Input Controls
Multiline Text Editor in p-Key Dialog
Symbol/Part Pin List in p-Key Dialog
PDF Output with Symbol/Part Notes
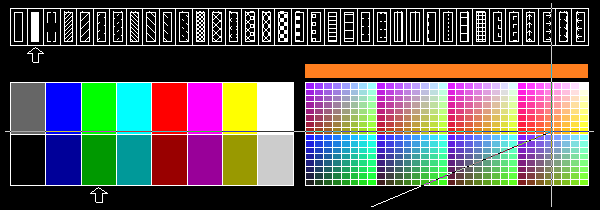
Layout Colour Palette extendend to 512 Colours
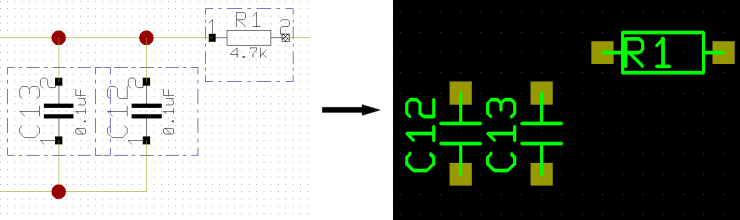
Layout Group Autoplacement according to Schematics (BAE HighEnd)
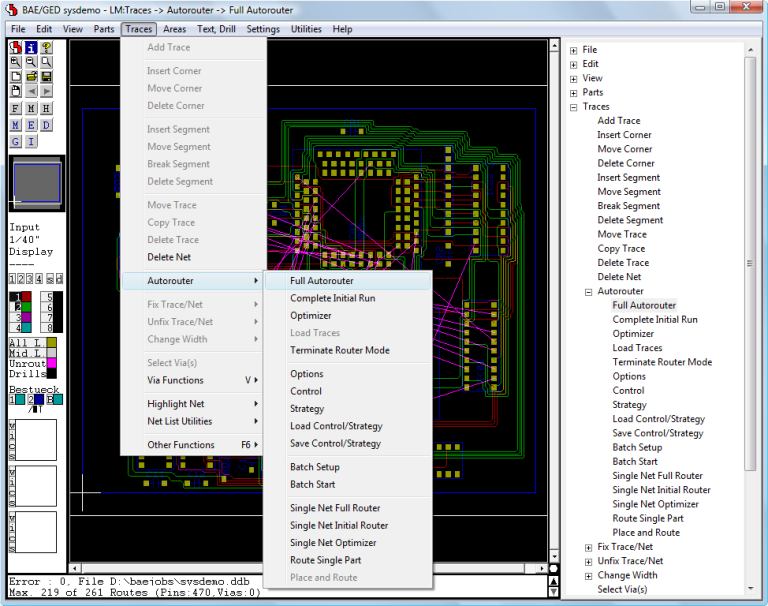
Autorouter Functions integrated to the Layout Editor
Automatic Drill Plan Generation with Drill Legend
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 7.4
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 7.4.
Contents
Treeview Menu Display Options
Left Treeview Menu Display
 |
Right Treeview Menu Display
 |
Toolbar Grid Display and Grid Selection
Improved Polygon Editor Interface
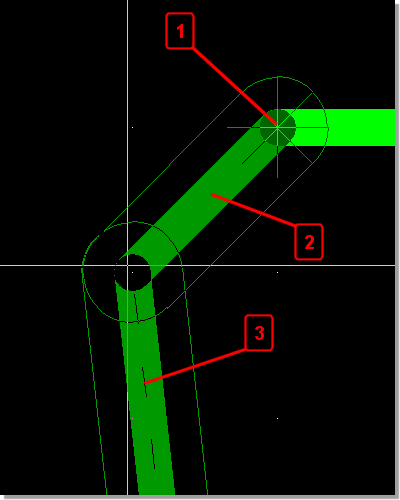 |
- Angle Direction Marker
- Solid display for segment placed by setting corner point
- Dashed display for segment processed after corner point
|
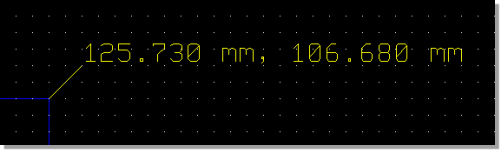
Coordinate Measuring
Separate X/Y Coordinates
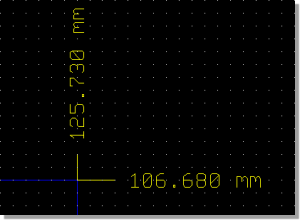 |
X/Y Coordinate Pair
 |
Symbol Browser with Logical Library Definition Display
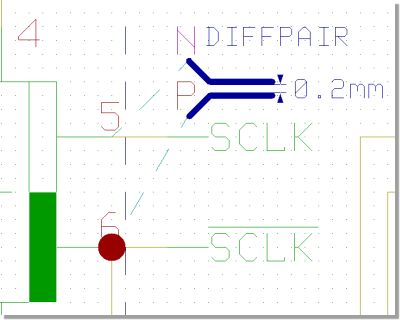
Differential Pairs
Schematic Plan Differential Pair Marker
 |
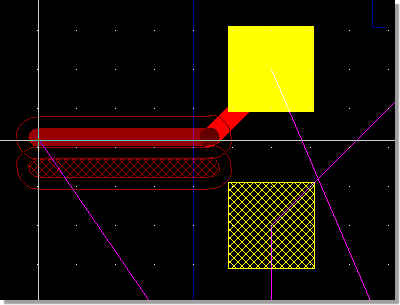
Layout Pair Partner Hatch Highlight and Parallel Trace Display
 |
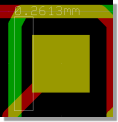
DRC Error Distance Display
DRC Error Marker
with Distance Display
 |
DRC Error Report
with Distance Display
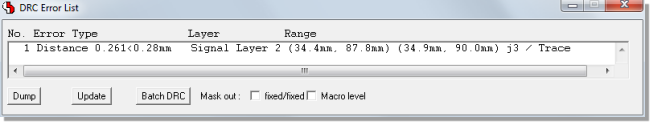 |
Postscript Output with Fixed Size Drilling Punch Hole
WRL Copper Output with transparent PCB Board
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 7.2
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 7.2.
Contents
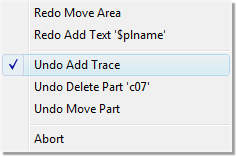
Undo/Redo List with Action/Function Display
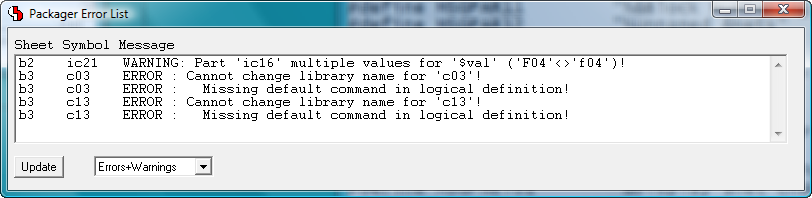
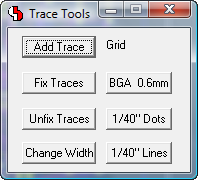
Packager Error List with Zoom to Schematic Symbols
Modeless Dialogs
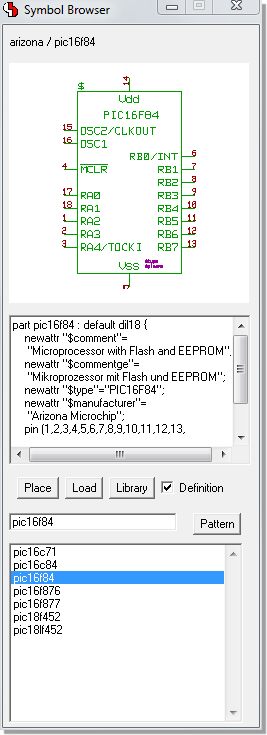
Symbol Browser
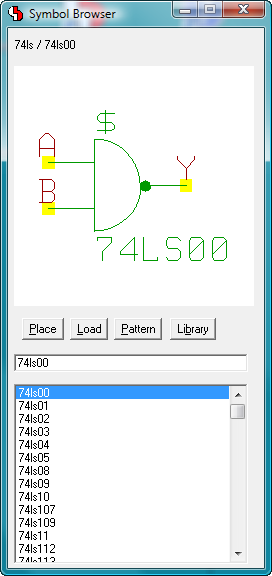 |
Draw Assistant
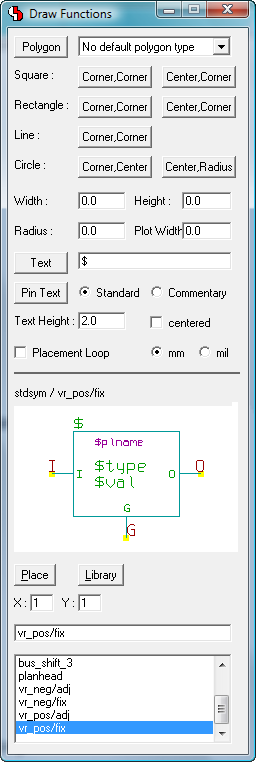 |
Favorites Dialog
 |
Display Grid Lines
Automatic Symmetric Polygon Generation
Create/Edit Polygon...
 |
...
 |
Layout Solder Side View
View Layout Component Side
 |
View Layout Solder Side
 |
Layout Net Highlight with Pattern Display
WRL Export with External 3D Part Models
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 7.0
Highlights
This document highlights some of the new features introduced with the Bartels AutoEngineer Version 7.0.
Contents
Bartels AutoEngineer Tooltips (Windows)
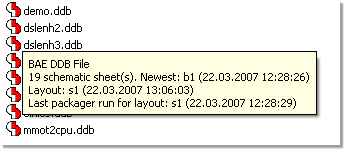
File Contents Info during File Selection | 
Toolbar Function Tooltips |
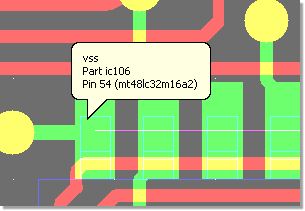
Element Info (optional) |
Schematic Editor - Symbol Logic Editor Dialog for Alternative Package Type Assignments
Layout Editor Polygon Combination
| 
Polygons |
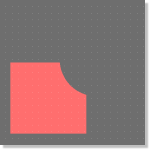
Cut Out |
Contour |
Intersection |
Layout Editor Thermal Stencil Pad Generation
Layout Editor Net Assistant
| 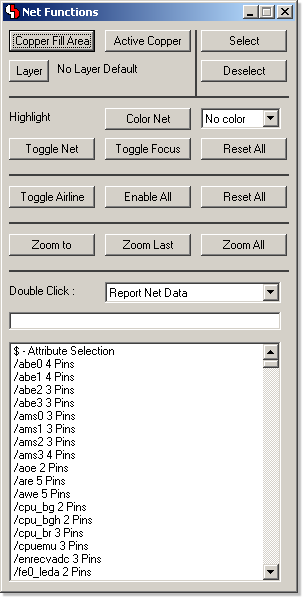 |
Modeless Layout Editor dialog with
net-specific
functions. |
Layout Editor Trace Beautifier
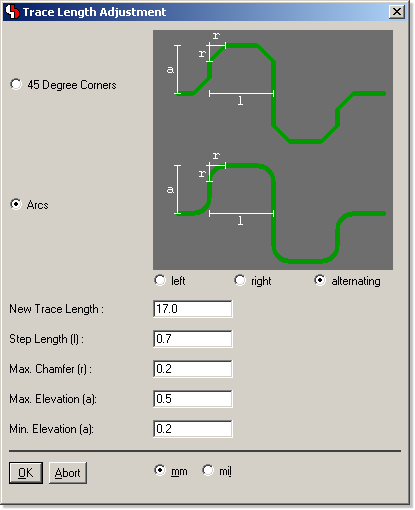
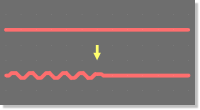
Layout Editor Trace Length Adjustment
Parallel Trace Signal Phase
| Signal Phase Shift Display
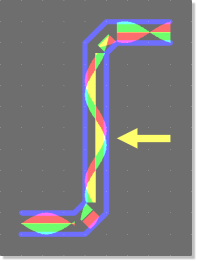 |
Phase Shift Compensation through Trace Length Adjustment
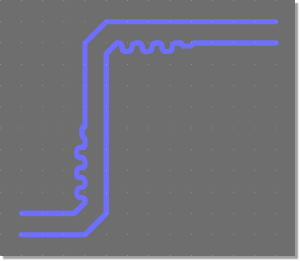 |
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 6.8
Highlights
Contents
Schematic Editor Symbol Selection with Symbol Preview
Layout Editor Part Selection with Part Preview
Toolbar Grid Favorites Configuration
Toolbar File Element Favorites Configuration
SCM Plot Preview with Pen Width
Layout Plot Preview with Pen Width
Graphic Cursor Info Tooltips
Polygon Point List Editor
Element-specific DRC Clearance Display Option
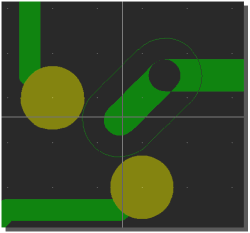
Gridless Trace DRC Snap
Gridless routing alongside obstacle edges
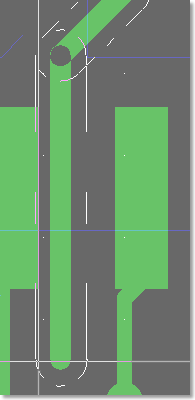 |
Trace centered between obstacles
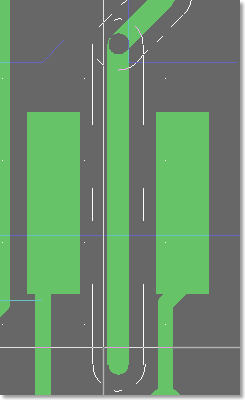 |
3-D Graphic Export to WRL/VRML1.0
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 6.6
Highlights
Contents
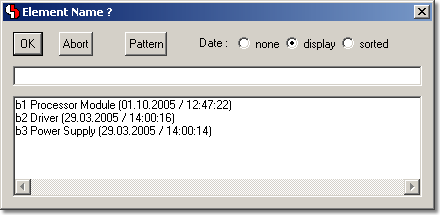
Element Selection with Comment and Date Display
Symbol Logic Editor with interactive Pin Assignment
Pin Assignments Table
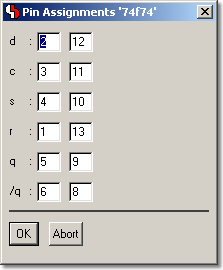 |
Pin Assignments graphically
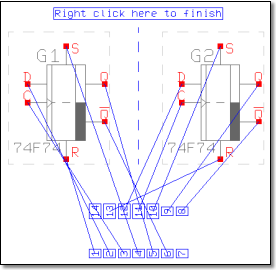 |
Automatic Bus Definition for Symbol Bus Pin Connections
Symbol Database with Symbol Preview
Symbol Context Menus programmable through Symbol Library Definitions
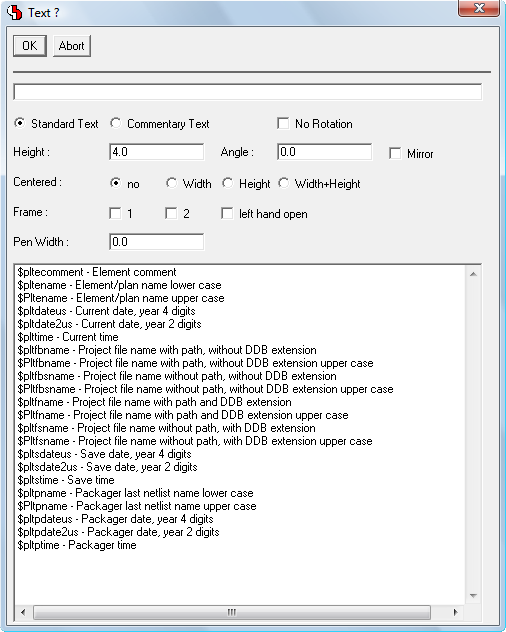
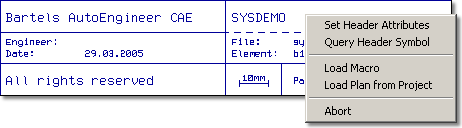
Toolbar Text Placement Function with Text/System Attribute List
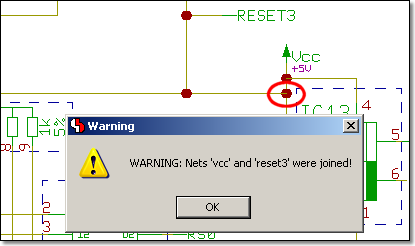
Warnings issued when connecting named Nets
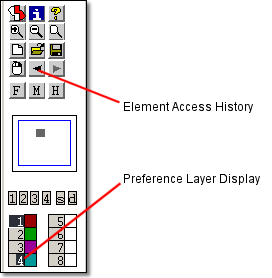
Toolbar with Element Access History and Preference Layer Display
Horizontal/Vertical Measuring Function
Trace Antenna Recognition
Element Manipulation Dialogs through p Key
Autorouter with improved SMD Pin Routing Algorithms
SMD Pin Routing prior to BAE V6.6
 |
SMD Pin Routing in BAE V6.6
 |
PDF Output with Layer Info (for Adobe Reader 6+)
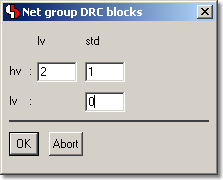
Dialog for Net Group DRC Assignments (BAE HighEnd)
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 6.4
Highlights
Contents
Project-wide Bus Tap Name Display
Labels with SCM Sheet Reference Display
Automatic SCM Block Symbol Generation for Hierarchical Designs
SCM Option for Direct Label to Pin Connections
SCM Option for connecting Connection Segments to Pin Rows
New Toolbar Functions
SCM Toolbar Buttons for Quick Drawing Function Access
 |
Layout Toolbar Buttons for Quick Documentary Layer Access
 |
Layout Toolbar Buttons for Color Table Management and Access
 |
Direct Coordinate, Angle, and Size Editing through Hotkey
Layout Editor Pick Point Display
Improved Layout Editor Segment Move Display
Layout Editor Hotkey Function for Trace Necking with DRC
Trace Bunch/Pattern Generation
Via Pattern Assignments to Fill Areas
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 6.2
Highlights
Contents
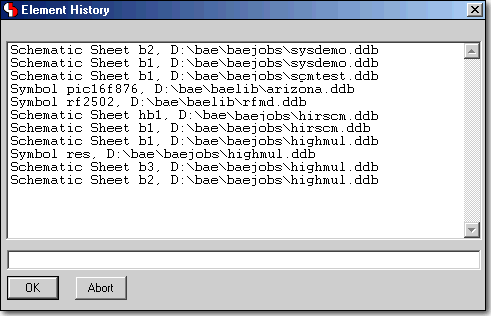
Element Processing History with Load Function
Macro Generator
Mathematical Expressions in Numeric Dialog Input Fields
Formula Input...
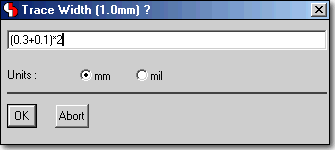 |
...is automatically calculated
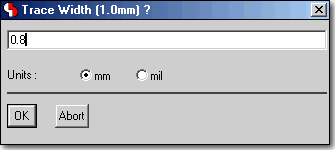 |
Windows/Motif Pulldown Menus with Shortcut Key Display
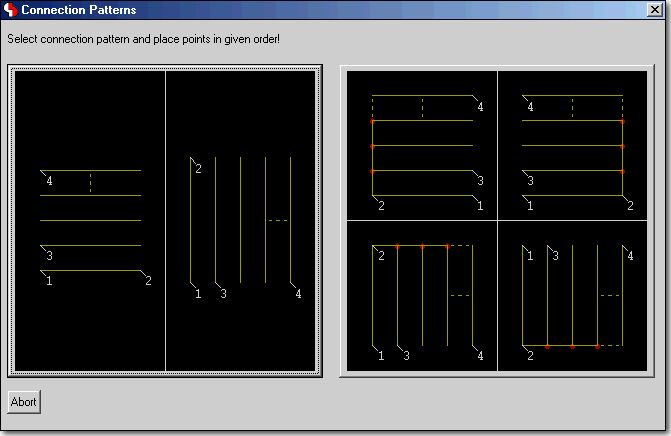
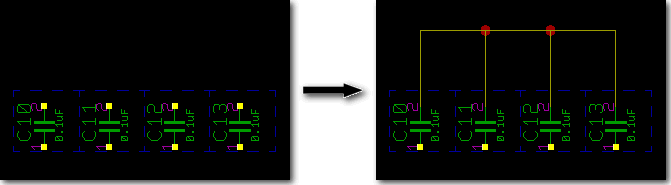
SCM Connection Pattern Generator
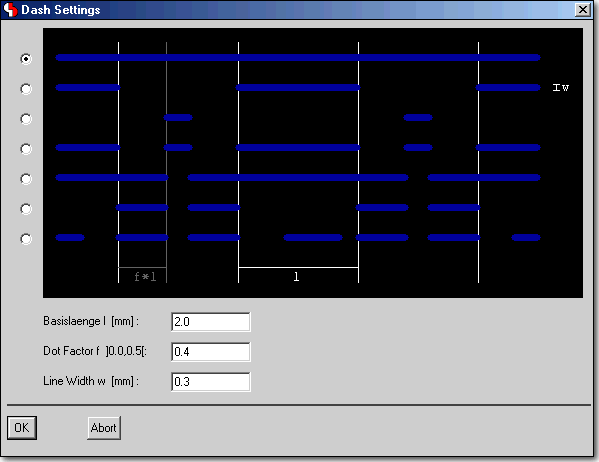
Polygon Dash Mode Settings Dialog in SCM and Layout
Layout Toolbar with Buttons for Preference Layer Selection and Signal Layer Color Assignment
Reference Line Display whilst Moving Layout Part Name and/or Attribute
Highlight Focus to display highlighted/erroneous SCM and/or Layout Elements exclusively
Highligh Focus Off
 |
Highlight Focus On
 |
Online Trace Length Display during Manual Routing
Programming EPS/PDF Output Configurations
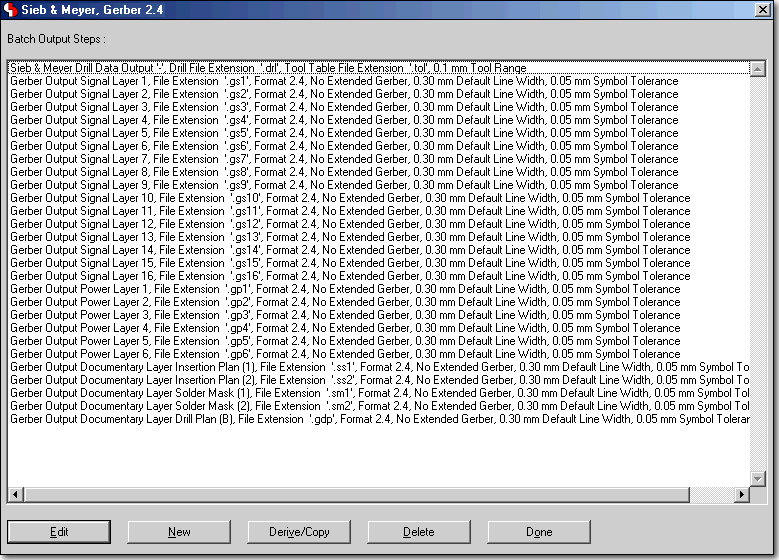
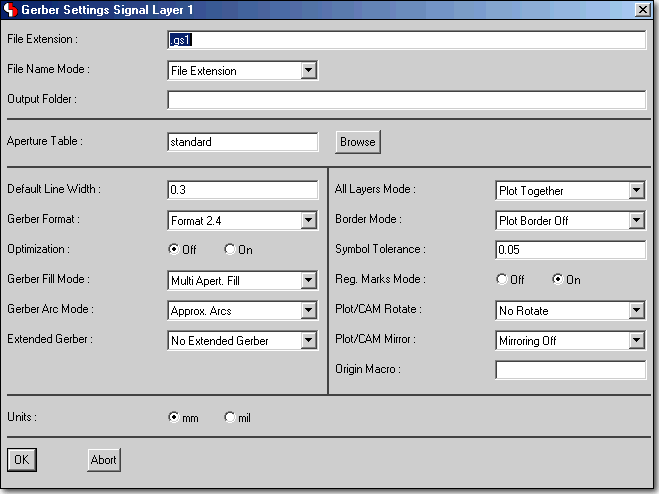
Programming CAM Batch Output Configurations
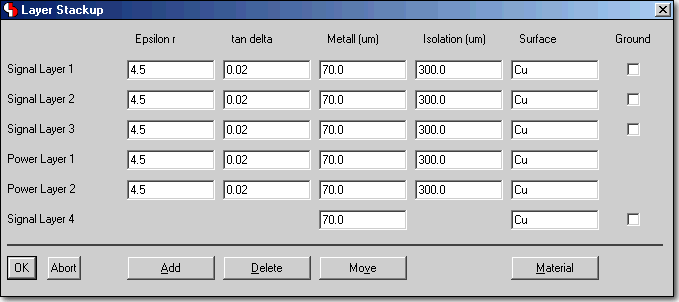
BAE HighEnd: Layout Layer Stackup Definition, e.g. for Impedance Calculations
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 6.0
Highlights
Contents
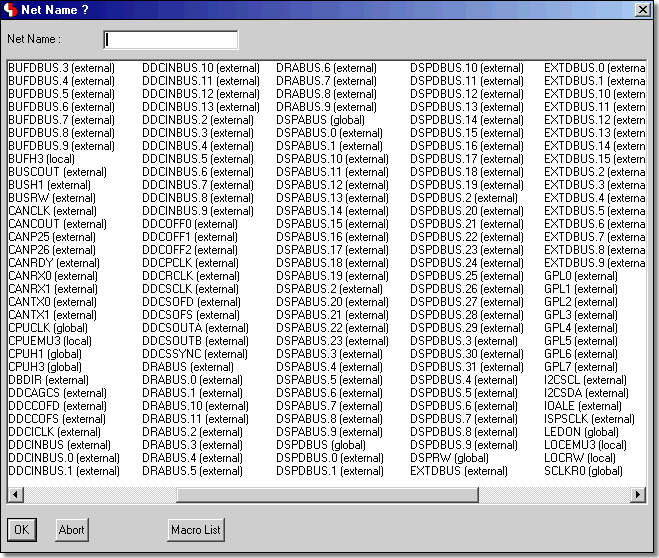
Schematic Editor with Project Net Name Selection Dialogs
Schematic Editor with Automatic Bus Tap Row Placement
Bus Tap Row Definition
 |
Bus Tap Row Placement
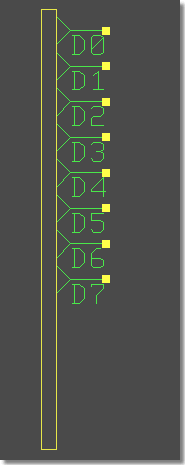 |
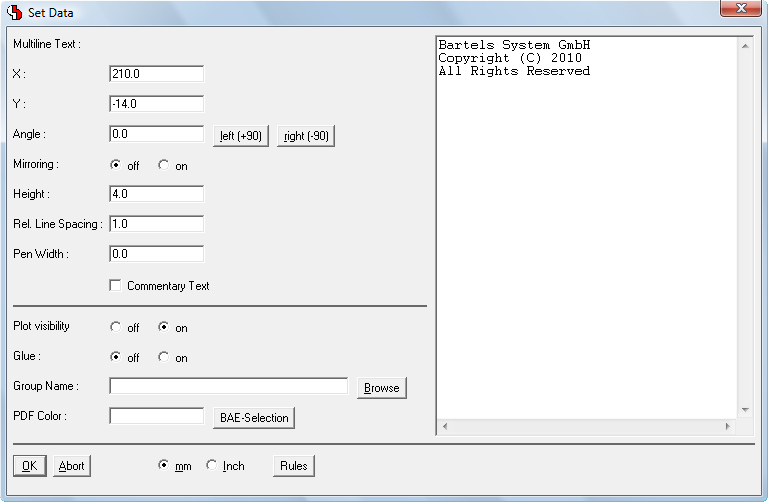
Multiline Text Processing in Schematics and Layout
Layout Editor with Dynamic Airline Display during Manual Routing
Autorouter Pin Connection Patterns
BGA Via Fanout Routing
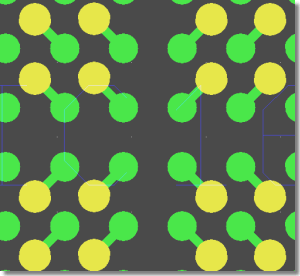 |
Microvias - Via-in-Pin Routing
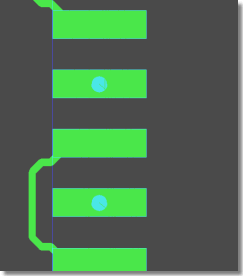 |
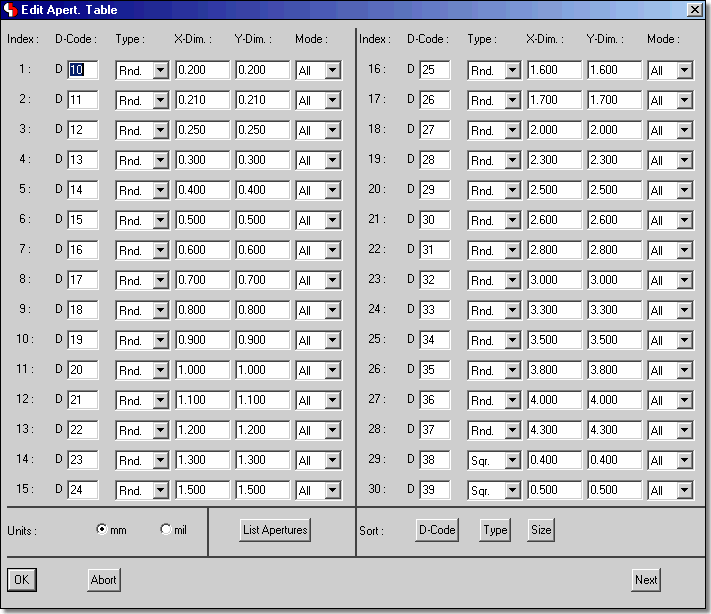
CAM Processor and CAM View Dialogs for Gerber Aperture Table Definitions
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 5.4
Highlights
Contents
Layout Display Pattern Settings
Increased Multilayer Visibility
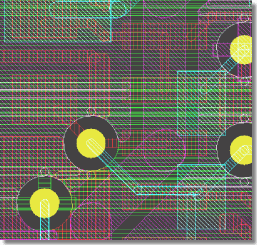 |
Overlapping Fill Area Outlines visible
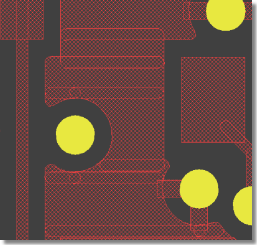 |
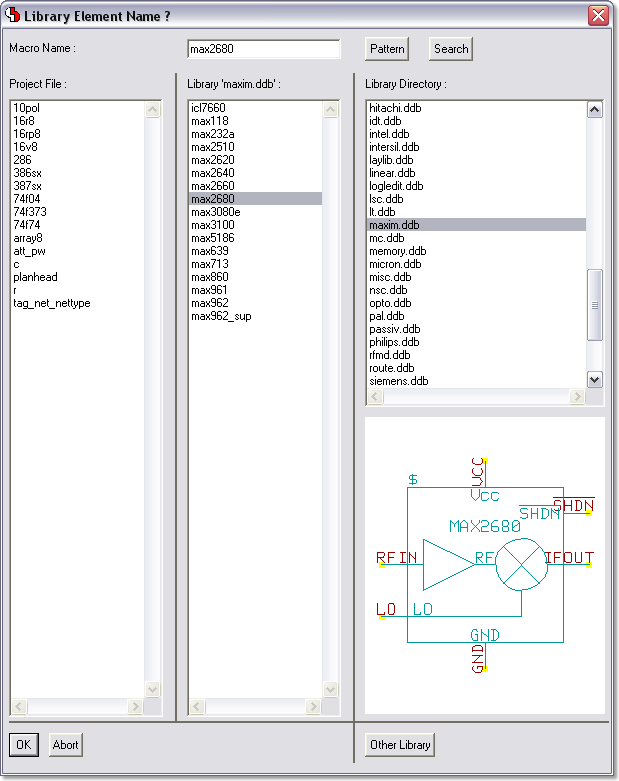
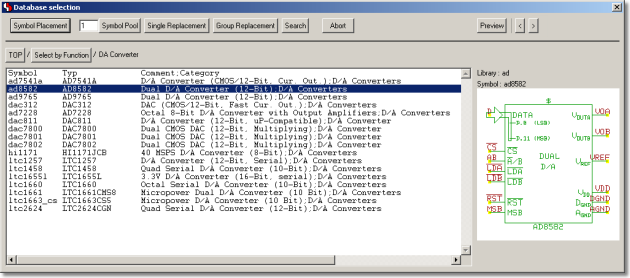
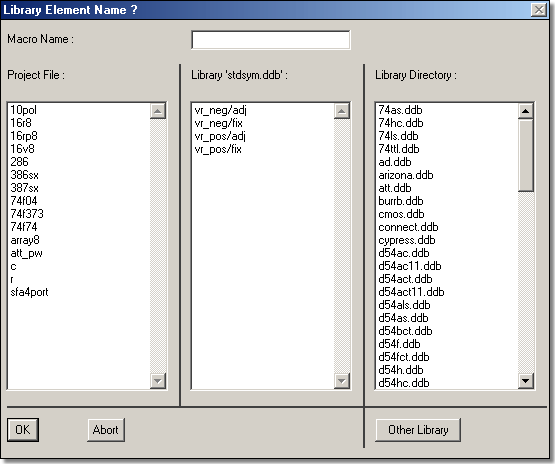
Library Element Selection Dialogs
Dialog for selecting Layout Parts and Part Sets for Placement
Dialogs for increased usability
SCM Text Classes for Visibility Control
only Values visible
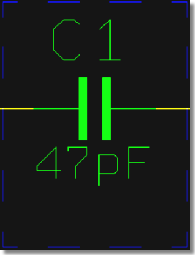 |
Values and Pin Names visible
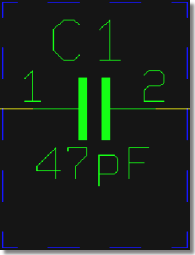 |
only Pin Names visible
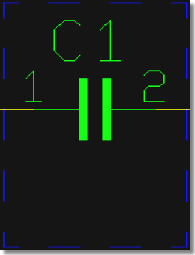 |
Copper Fill Cutouts on Alternative Layers
e.g., for Milling Contour Generation
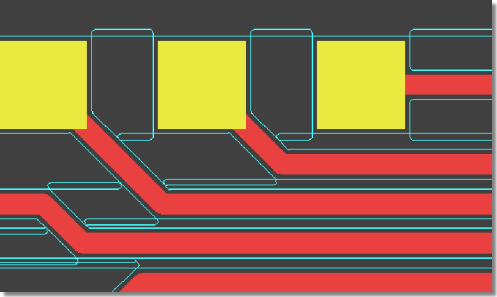 |
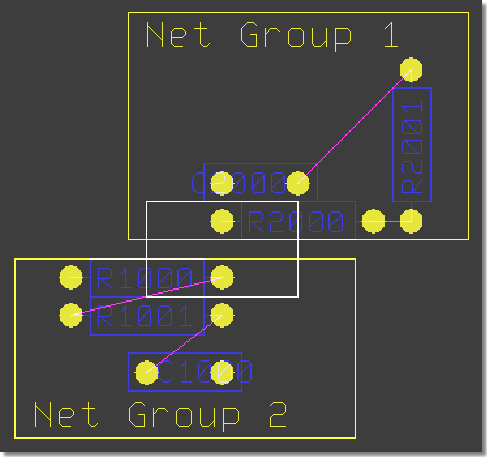
BAE HighEnd: Minimum Distance Check between Net Groups
Bartels AutoEngineer®
Version 5.0
Highlights
Contents
Real-time Design Rule Check during Manual Routing
Valid Via Position Display during Manual Routing
Pin/Gate Swap
Displaying swappable Pins/Gates...
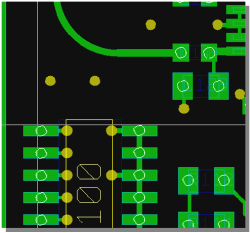 |
...and possible Swap Partners
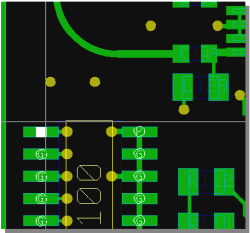 |
Height Design Rule Check
DRC Error Display
DRC Error Listing...
 |
...and Zoom to Selected Error
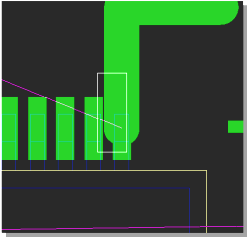 |
Automatic Keepout Area Generation for Board Outline and Milling Contours
Element Selection for Multiple Elements at Pick Position
Bartels AutoEngineer® HighEnd
Advantages and Features
Contents
Mincon Generation (Airline Calculation)
delay in BAE Professional
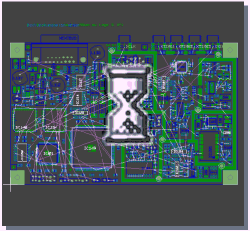 |
instant response in BAE HighEnd
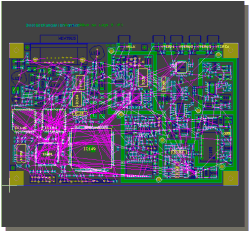 |
Power Signal Structure Processing
deleting power signal area
in BAE Professional
 |
deleting power signal area
in BAE HighEnd
 |
Short-Circuit Display
highlighting all short-circuit net elements
in BAE Professional
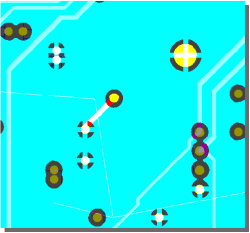 |
selective short-circuit highlight
in BAE HighEnd
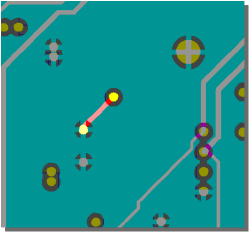 |
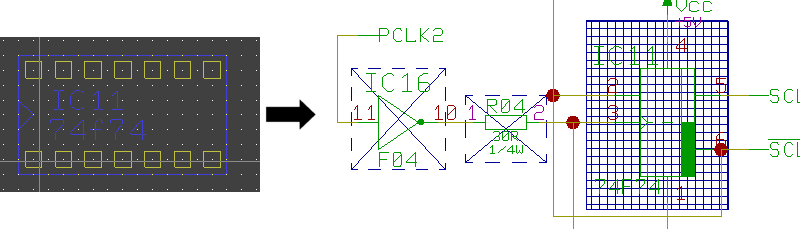
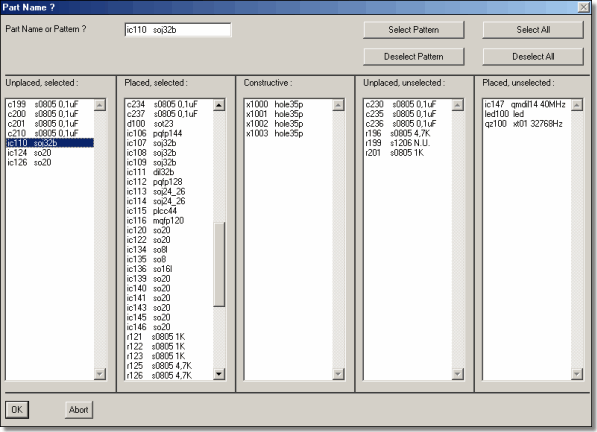
Part Search
layout part selection...
 |
...and automatic zoom to SCM symbol
 |
Simultaneous Net Highlight in Schematics and Layout (Cross-Probing)
Group Selection Transfer
SCM symbol group selection...
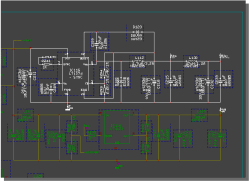 |
...to select corresponding layout parts
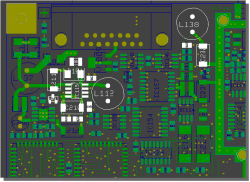 |
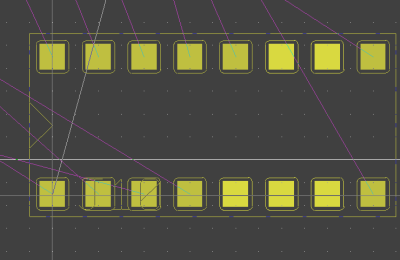
Physical SCM Parts Placement
select SCM symbol...
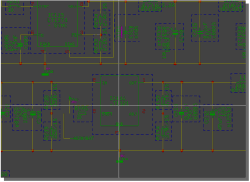 |
...and place corresponding layout part
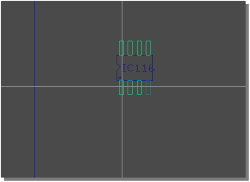 |
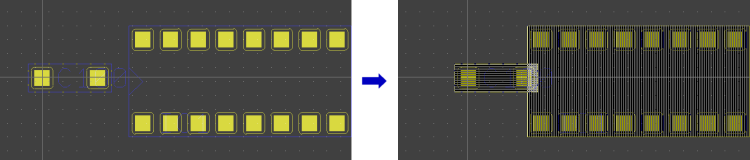
Select Layout Placement Part Sets from SCM Symbol Groups
group-select SCM symbols and...
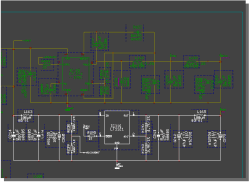 |
...autoplace corresponding layout part set
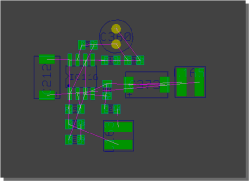 |
Layer-specific Clearance Settings for DRC and Automatic Copper Fill
CAM Processor to suppress output of unused indside layer pads
Checking high-frequency Net Shielding through minimum Ground Plane Intersection
Net Group Clearance Check
Layout Layer Stackup Definition, e.g. for Impedance Calculations
Dialog for Net Group DRC Assignments
Layout Group Autoplacement according to Schematics
Placed Symbol Indication
Bartels AutoEngineer® - Product Information
© 1985-2025 Oliver Bartels F+E